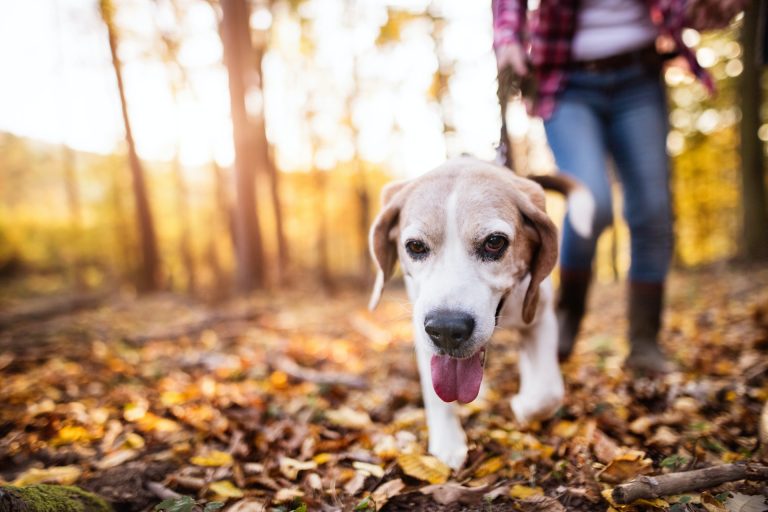
Nine News/Georgie Purcell via X/The Conversation
Earlier this week, Channel Nine published an altered image of Victorian MP Georgie Purcell that showed her in a midriff-exposing tank top. The outfit was actually a dress.
Purcell chastised the channel for the image manipulation and accused it of being sexist. Nine apologised for the edit and blamed it on an artificial intelligence (AI) tool in Adobe Photoshop.
Generative AI has become increasingly prevalent over the past six months, as popular image editing and design tools like Photoshop and Canva have started integrating AI features into their programs.
But what are they capable of, exactly? Can they be blamed for doctored images? As these tools become more widespread, learning more about them and their dangers – alongside opportunities – is increasingly important.
Read more:
AI to Z: all the terms you need to know to keep up in the AI hype age
What happened with the photo of Purcell?
Typically, making AI-generated or AI-augmented images involves “prompting” – using text commands to describe what you want to see or edit.
But late last year, Photoshop unveiled a new feature, generative fill. Among its options is an “expand” tool that can add content to images, even without text prompts.
For example, to expand an image beyond its original borders, a user can simply extend the canvas and Photoshop will “imagine” content that could go beyond the frame. This ability is powered by Firefly, Adobe’s own generative AI tool.
Nine resized the image to better fit its television composition but, in doing so, also generated new parts of the image that weren’t there originally.
The source material – and if it’s cropped – are of critical importance here.
In the above example where the frame of the photo stops around Purcell’s hips, Photoshop just extends the dress as might be expected. But if you use generative expand with a more tightly cropped or composed photo, Photoshop has to “imagine” more of what is going on in the image, with variable results.
Is it legal to alter someone’s image like this? It’s ultimately up to the courts to decide. It depends on the jurisdiction and, among other aspects, the risk of reputational harm. If a party can argue that publication of an altered image has caused or could cause them “serious harm”, they might have a defamation case.
Read more:
Australia plans to regulate ‘high-risk’ AI. Here’s how to do that successfully
How else is generative AI being used?
Generative fill is just one way news organisations are using AI. Some are also using it to make or publish images, including photorealistic ones, depicting current events. An example of this is the ongoing Israel-Hamas conflict.
Others use it in place of stock photography or to create illustrations for hard-to-visualise topics, like AI itself.
Many adhere to institutional or industry-wide codes of conduct, such as the Journalist Code of Ethics from the Media, Entertainment & Arts Alliance of Australia. This states journalists should “present pictures and sound which are true and accurate” and disclose “any manipulation likely to mislead.”
Read more:
Should the media tell you when they use AI to report the news? What consumers should know
Some outlets do not use AI-generated or augmented images at all, or only when reporting on such images if they go viral.
Newsrooms can also benefit from generative AI tools. An example includes uploading a spreadsheet to a service like ChatGPT-4 and receiving suggestions on how to visualise the data. Or using it to help create a three-dimensional model that illustrates how a process works or how an event unfolded.
What safeguards should media have for responsible generative AI use?
I’ve spent the last year interviewing photo editors and people in related roles about how they use generative AI and what policies they have in place to do so safely.
I’ve learned that some media outlets bar their staff from using AI to generate any content. Others allow it only for non-realistic illustrations, such as using AI to create a bitcoin symbol or illustrate a story about finance.
News outlets, according to editors I spoke to, want to be transparent with their audiences about the content they create and how it is edited.
In 2019, Adobe started the Content Authenticity Initiative, which now includes major media organisations, image libraries and multimedia companies. This has led to the rollout of content credentials, a digital history of what equipment was used to make an image and what edits have been done to it.
This has been touted as a way to be more transparent with AI-generated or augmented content. But content credentials are not widely used yet. Besides, audiences shouldn’t outsource their critical thinking to a third party.
In addition to transparency, news editors I spoke to were sensitive to AI potentially displacing human labour. Many outlets strive to use only AI generators that have been trained with proprietary content. This is because of the ongoing cases in jurisdictions around the world over AI training data and whether resulting generations breach copyright.
Read more:
How a New York Times copyright lawsuit against OpenAI could potentially transform how AI and copyright work
Lastly, news editors said they are aware of the potential for bias in AI generations, given the unrepresentative data AI models are trained on.
This year, the World Economic Forum has named AI-fuelled misinformation and disinformation as the world’s greatest short-term risk. It placed this above even disasters like extreme weather events, inflation and armed conflict.

World Economic Forum, Global Risks Perception Survey 2023–2024
Because of this risk and the elections happening in the United States and around the world this year, engaging in healthy scepticism about what you see online is a must.
As is being thoughtful about where you get your news and information from. Doing so makes you better equipped to participate in a democracy, and less likely to fall for scams.
![]()
T.J. Thomson receives funding from the Australian Research Council.